Digital manufacturing is a method of production in which computer technology manufactures products in a desired style or quantity with little or no involvement from humans. The process is known by a variety of other names, including direct digital manufacturing, rapid manufacturing, instant manufacturing, and on-demand manufacturing. The technology utilized in this approach offers companies the ability to develop prototypes and plan and customize the production process from start to finish.
The creation of products through the mode of digital manufacturing is employed by businesses in a wide array of industries. The aerospace, automobile, consumer goods, energy, fashion, high tech, industrial, medical, military, packaging, and shipbuilding industries are just a sampling of the types of companies who use this type of manufacturing. It is especially popular with tool manufacturers as it allows for the on-demand production of direct tooling inserts.
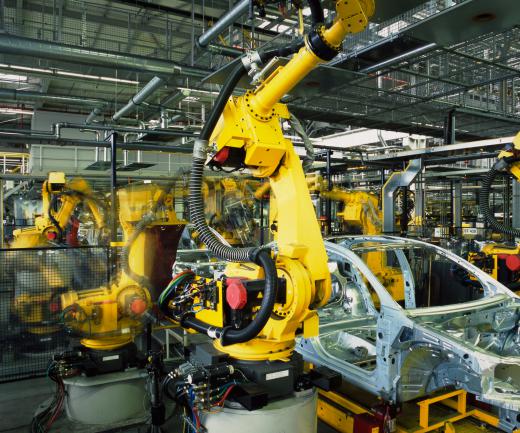

There are numerous advantages to utilizing digital manufacturing over more traditional processes. Instead of producing mass amounts of a product, this type of manufacturing ensures only a predetermined amount is made. This helps in maintaining an efficient level of energy usage and guarantees material waste is kept to an absolute minimum. By allowing manufacturers to set up the precise quantity of products to be created, a business is given greater control over everything from production cost to product quality.
In general, a product created by digital manufacturing travels through the production process at a much faster rate. Unnecessary steps and supplementary procedures can be cut down or omitted entirely from the course of manufacturing. This helps a product make it to the consumer in timelier manner, and, in some cases, at a much lower cost to the manufacturer.

Digital manufacturing also has the distinct benefit of being able to process and refine complicated design systems in a short period of time. Through the latest technologies, a digital set-up can make for speedy creation and enhancement of a product. This is accomplished by a streamlining of existing designs and geometries, automatically condensing the process into as few steps as are allowable.
There are several companies that produce manufacturing systems intended to cover all aspects of the production process. From product design and production planning to product life-cycle management and the determination of worker safety, these systems encompass all of the key steps of the manufacturing course. Many utilize easy-to-use interfaces and a simple Internet connection to simulate, plan, and execute the entire procedure.
