Radiographic testing is a form of materials testing that uses electromagnetic waves to check for defects in an object. This testing technique can be used on everything from metal or wood, and is particularly effective on things like steel or composite materials. Radiographic testing is a form of nondestructive testing (NDT). During NDT, the material being inspected remains intact, and is not subject to cutting, boring, or other disturbances.
This test method involves using an X-ray machine to send electromagnetic radiation through an object. This is typically done using a hand-held X-ray device, but may also be performed using gamma rays. As the photons from these waves enter the object, some of the energy from the waves is absorbed into the material. Others pass through the object and exit through the other side. By measuring changes in these waves as they leave the material, testers can check for flaws in the object.
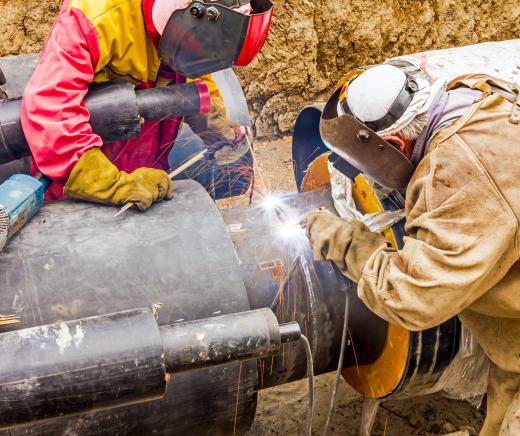

Radiographic testing provides a great deal of information to test professionals and engineers. It can help to verify the thickness of a material, as well as its structural makeup. Radiographic testing also alerts testers to internal cracks, voids or air pockets within the material. This type of testing may also point out weak spots that could lead to failure over time.
One of the primary advantages to radiographic testing is that it provides a film record of the test results. These results appear similar to a medical X-ray, and can help users evaluate or diagnose the material. Dark spots on the film represent energy that was not absorbed by the material, and generally indicate a flaw or defect. These images can be used to repair an object or to help users find a more effective manufacturing technique. Repeat testing allows users to keep images on file and compare them to spot changes in an object over time.
Radiographic testing represents a popular method for testing welds and seams in metalwork or composites. Like other nondestructive testing techniques, this test method allows engineers to verify the effectiveness of a weld without disturbing the material. This process is also widely used to inspect building materials, spacecraft and satellite components.
Those who pursue employment in this field should be aware of the potential safety risks associated with radiographic testing. This process exposes workers to dangerous radiation, which can have serious health consequences. All testing personnel should undergo training and follow proper safety procedures when performing these tests.
