An electric voltmeter is an electrical device used to measure the voltage or current moving between two points or contacts within an electrical circuit. Voltmeters are made in a number of different formats, each of which are used for different applications. Electronic voltmeters can be either analog or digital. They are designed to undergo direct contact with electrical power and energy across a circuit in order to measure the capacity, resistance, tolerance, voltage and electrical potential of that circuit.
Some voltmeters are created as permanent fixtures within circuits and located on circuit panels where they are used to determine the constant current that is traveling between two points within the circuit. Portable voltmeters, on the other hand, are contained within small, usually hand-held devices that utilize two external contact points. These contact points may be placed on two different circuit contacts to display the voltage or electrical potential of that circuit.
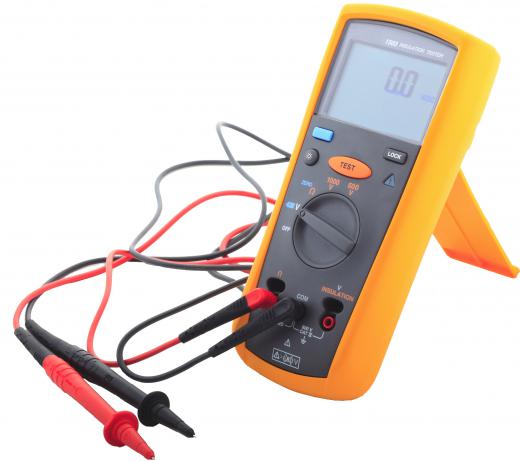

An electronic voltmeter can test the electrical potential of direct and alternating currents. An electronic voltmeter is also capable of calculating both currents for voltage measurements within a circuit. Due to the fact that an electronic voltmeter is able to measure different aspects of a circuit, and is able to do so no matter what power is supplied to the circuit, such voltmeters are also considered to be multimeters. The voltmeter is only able to take a measurement when the circuit is completed, meaning power must be flowing through the circuit for the meter to take a reading of the circuit’s voltage potential.

Other uses and applications associated with an electronic voltmeter include circuit testing. The tests check for the presence of voltage or power before an electrical engineer or electrician begins working with the circuit. An electronic voltmeter can also be used to provide students in an electrical laboratory with visual examples of where voltages and energy may be stored that could be dangerous.
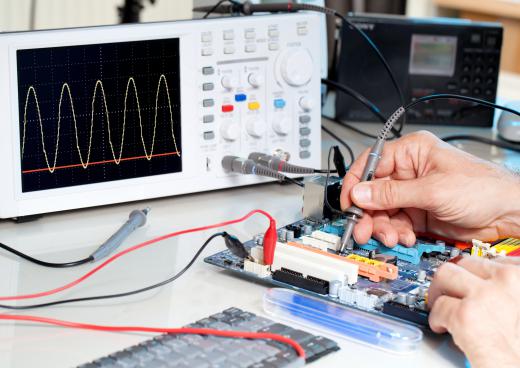
Digital and analog methods are not the only methods of electronic voltmeter usage, however. There are electrostatic voltmeters, that can measure the electrical potential of a circuit without any physical lead contact with the circuit itself. An oscilloscope, for example, is a voltmeter that is considered to be much more advanced than a regular voltmeter because it has the ability to track the number of times a current changes its course or direction in an AC circuit. A typical voltmeter doesn’t have the ability to take measurements that quickly.
The most frequently purchased and used voltmeters are referred to as solenoid voltmeters. These voltmeters are durable and able to withstand a significant amount of abuse. The durability stems from the simplicity of their design.
