Medical waste refers to any materials that are produced in a medical environment as a result of treatment, diagnostics, testing, and any other tasks performed in such a location. There are several main types of medical waste: biohazardous, solid, liquid, anatomical, pharmaceutical, chemotherapy and sharps waste. Each of these follows its own distinct medical waste disposal codes.
Biohazardous waste comprises nearly anything that has come in contact with a patient’s body and thus has been exposed to bodily fluids and illnesses, if present. This can include things such as human excrement, tissue samples, or used swabs and bandages. Proper medical waste disposal for bio hazardous materials require that they be placed in a labeled bag and then sealed closed. Then, the bag must be placed in a leak proof container and labeled on all sides as biohazardous.

Solid waste is usually steam sterilized and then disposed of in the same fashion as any other trash or waste. This type of medical waste consists of things like gloves, unsoiled paper gowns, and empty containers. Liquid waste requires a different kind of medical waste disposal. Blood, urine, and other fluid or near-fluid materials must be decontaminated using an agent such as chlorine, and then sent through the sewer system through specialized drains where it will be further treated with all other waste water.
Another type of medical waste involves the disposal of any anatomical human remains. This does not include the deceased, but refers to things like organs, tissue matter, or removed limbs. These things are required to be incinerated, usually on-site.
Chemotherapy waste is disposed of separately and must be labeled as CHEMO waste. Radioactive waste is chemically treated and then transported to specialized facilities. There are also pharmaceutical waste products that must be disposed of, usually by putting them into a cardboard box that is taped shut, and then tossed in with the regular solid waste.
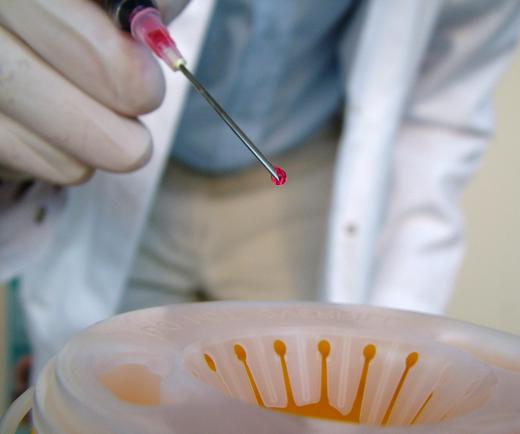
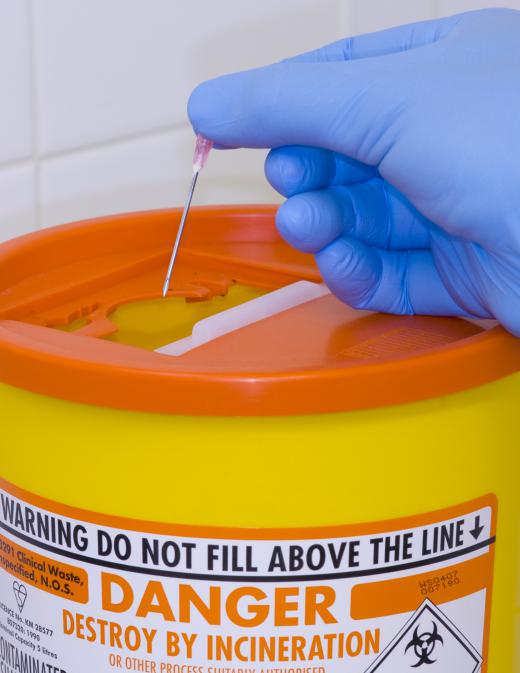
Medical waste disposal also requires the containment of sharps waste. This includes things like needles, syringes and blades used during surgery. Because these items can be potentially contaminated by diseases that could be transferred to others, special care is taken in their disposal. Used sharps waste must be placed in a puncture- and leak-proof container and incinerated. Non-used sharps waste is taped and thrown in a regular garbage bag.

For waste that cannot be dealt with on site, there are special facilities available that pick up and transfer waste for proper disposal. These wastes may include biohazard and anatomical waste, as well as used sharps waste. In the event that a hospital does not have an incinerator on site, these items will be placed in leak and puncture proof containers and transported to the proper facilities.
