Phosphor bronze is a copper alloy that consists mostly of copper with a significant percentage of tin and a smaller percentage of phosphorous. This kind of bronze is strong, has a fine grain, and is easily molded into a variety of shapes. The many benefits of phosphor bronze over some other metals have led to its use in springs, bolts and ship’s propellers. Dental bridges, guitar strings, and many other instruments also might include some elements of phosphor bronze.
Springs are often made out of phosphor bronze because the alloy can withstand repetitive motion and still maintain shape. Large springs used in industrial machinery are often made out of phosphor bronze because they also are more resistant to strain than non-alloy components. These features also encourage the use of phosphor bronze to make structural components such as fasteners.

Bolts are often made out of phosphor bronze, because they can be expected to last without breaking down. The industrial uses of such bolts include fasteners for machines, structures and within electrical systems because of their high conductivity. Industrial machinery that regularly handles chemicals also can benefit from the use of this bronze, because it also is resistant to many chemicals.
Resistance to corrosion means phosphorous bronze can be especially useful for making ship’s propellers. The combination of metals and phosphorous often increases the copper’s resistance to water, salt and chemicals. The marine vessels industry often uses this alloy to improve product quality, though less expensive metals are often used, as well. Constant exposure can break down the metal over time, especially in harsher conditions, but much slower than it would many other metals.
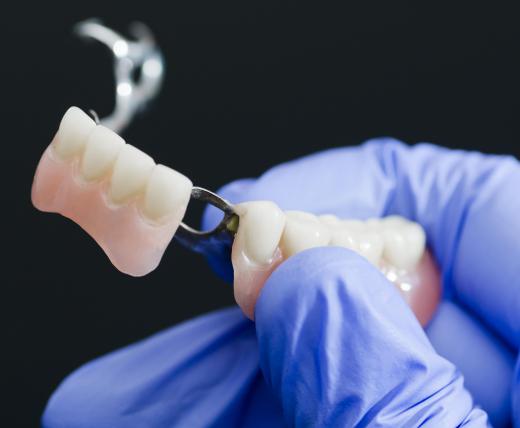
Dental bridges also benefit from this characteristic resistance to corrosion. Though many dental bridges must be customized, certain parts can be manufactured on an industrial scale. Used to provide the basis for tooth implants, dental bridges made with this alloy will generally maintain their shape over time. Phosphorous bronze can be used to make partial or full implants and might be used to create supports for teeth made of materials such as ceramics.
Guitar strings are often wrapped in phosphor bronze wire to provide resistance to corrosion, which can deaden the sound being produced. Many industrial manufacturers of guitar strings use this alloy for a majority of their products. Resistance to moisture and oils associated with routine playing also makes it useful for wind instruments such as trumpets, rhythmic instruments such as cymbals, and many other instruments that include metal components.
