There are a number of types of thin film devices. This technology is used extensively in optical devices and semiconductors, though there are other applications as well. The extremely thin films used are created out of a variety of different metals and compounds, each with its own properties and applications.
In the field of optics, the thin film devices used are in the form of various optical filters. These filters are common in photography, telescopes and microscopes, and different types of thin films are deposited on glass or plastic filters which are designed to change the properties of the light passing through. Some filters may enhance light as it is refracted through the lens while others may dampen it. Filters can be made to affect only a narrow range of wavelengths or the entire spectrum of visible light.

A semi-conductor is another possible type of thin film device. These devices conduct low levels of electrical current. Thin film semi-conductors can be made out of different materials which determine the amount and level of current that the device conducts. Devices such as these are used in the fields of microelectronics, micro-circuitry and integrated circuits.
One thin film device that many people are familiar with is the mirror. Many mirrors are made of a thin film of a reflective substance, such as aluminum, which is attached to a glass substrate. The aluminum reflects an image that is passed through a pane of glass. Double-sided mirrors and two-way mirrors are two other types of thin film device that use a glass substrate and a thin film of reflective metal.
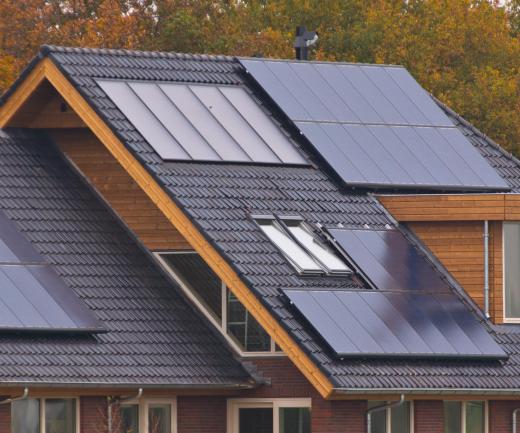

Another type of thin film device that is quite common is the dye-sensitized solar cell. These solar cells use a thin film semiconductor containing a dye that is sensitive to radiation from the sun. When the dye absorbs photons, it creates an electric charge which passes through the semiconductor, transferring energy to a battery attached to the solar cell.
In medicine, new types of thin film devices are being introduced to the market. Thin films can be used to deliver medicine when dissolved on the tongue or inside the stomach or intestines. The film allows the medication to enter the bloodstream quickly without the need to swallow pills or liquid suspensions. These thin film devices offer an alternative to traditional medication delivery methods and can help patients who are unable to swallow.
