There are many pulley dimensions to be obtained from a pulley system, including the length of the belt, the velocity ratio of the system, and the pitch diameter of the belt. The velocity ratio is calculated using the rotations-per-minute (RPMs) or circumferences of the driver and driven pulleys. Although the pitch diameter of the belt is not often needed, this dimension can be difficult to determine.
The first dimension to measure is the length of a belt between two pulleys. A simple way to do this is to take a piece of string, wrap it around the two pulleys and mark where the end of the string touches another part of the string. Take a measuring stick or measuring tape and measure from the end of the string to the marked part of the string.
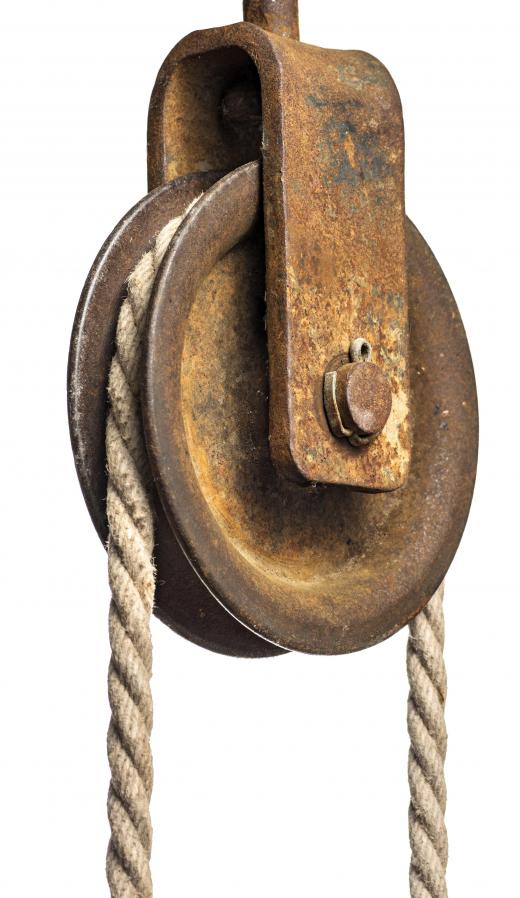

The next of the pulley dimensions you can measure is the velocity ratio; to obtain this measurement, you can use either the RPMs or circumferences of the driver pulley and the driven pulley. For a pulley system like those found in an automobile engine, the RPM can be found using print or online manuals of a particular engine, or the use of a tachometer. You will likely already know the RPMs of the driver pulley, but not the driven pulley. If you know the RPMs of both pulleys, you can divide the RPM of the driver pulley by the RPM of the driven pulley. Otherwise, you must use the circumferences of the driver pulley and driven pulley to determine the velocity ratio.

Obtain the circumferences of both the driver pulley and the driven pulley by measuring the radii of both pulleys. To determine the radius, measure widthwise from one edge of the pulley wheel to the center. Multiply the radius by 2 π (pi) and you will have the circumference of the pulley wheel. Do this for both pulley wheels to obtain two circumference values. Then, divide the circumference of the driven pulley by the circumference of the driver pulley to obtain the velocity ratio of the system.
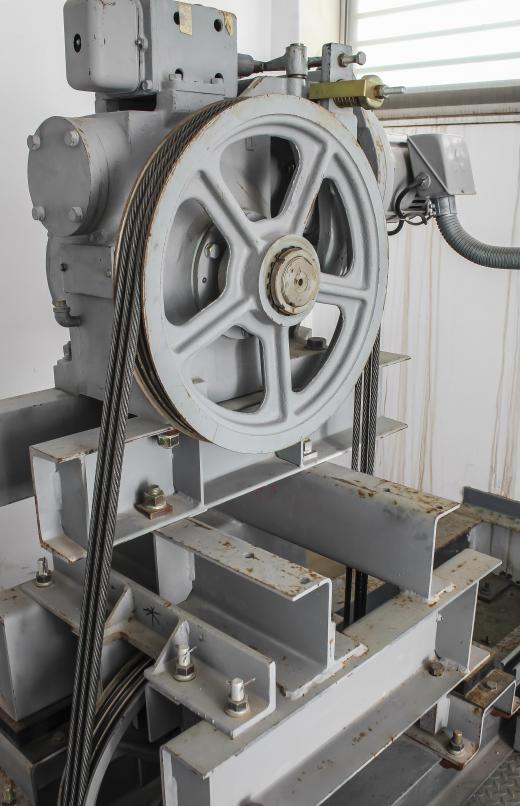
The velocity ratio is a one of the essential pulley dimensions to know for any pulley system found in machinery like automobile engines or industrial conveyor belts. It is used to determine how much work is performed and how much power is exerted in a system, which is known as mechanical advantage. As an example of this concept, bicycles have multiple gear settings — or velocity ratios — to increase or decrease the workload a biker uses to pedal. In automobile engines, the velocity ratio is used to increase output torque or output speed.

One of the pulley dimensions you may need, but not necessarily be able to obtain, is the pitch diameter of a belt. This is the diameter of the threads found inside the belt. It is possible, but not practical, to measure this. Instead, you can consult a manual on a particular piece of machinery or use an online calculator with the system's measured pulley dimensions.
